Immersive technologies are at the forefront of blurring the boundaries between real and virtual existence, intricately focusing on precision and details to develop the best spatial 3D experience called the metaverse. The immersive technologies are collectively known as ‘extended reality,’ abbreviated as XR.
The meaning of extended reality and the field’s understanding is still evolving with the consistent development in human-computer interactions. XR is a dynamic field whose discoveries can be applied to different areas such as entertainment, marketing, real estate, training and remote work.
Technologists envision the convergence of the smartphone, mobile virtual reality headset, and augmented reality technology like AR glasses into a single XR wearable. XR could probably replace all the other screens in our lives, like the television. Most experts in the field believe that mobile XR has the potential to become one of the world’s most prevalent and groundbreaking computing platforms—similar to the smartphone today.
Extended reality offers limitless opportunities; therefore, extended reality companies must develop a safe and conducive ecosystem to utilize its full potential.
In this article, we’ve covered the meaning of extended reality, the various augmented and virtual reality trends, examples and applications of XR, and other interesting information. Read till the end to learn more.
What Do You Mean By Extended Reality?
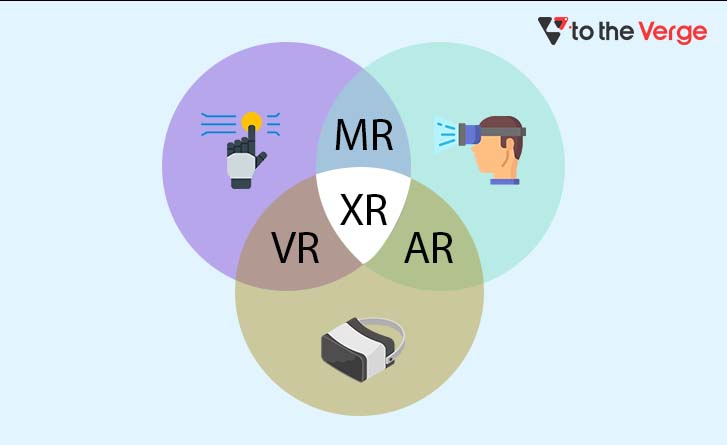
Extended Reality is a term that encapsulates specific individually popular technologies like Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), and everything in between. Although AR and VR offer a wide range of revolutionary experiences, the same underlying technologies are powering XR.
It combines real-life objects and computer-generated graphics seamlessly to fabricate a virtual environment that matches the reality of humans. In simple terms, XR is a blanket term for Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR) combined.
Extended reality or XR creates collaborative environments where humans are enabled to interact with virtual elements fabricated using computer technology and other machine wearables. The levels of virtuality range vary depending on the level of immersiveness.
In some instances, there could only be a partial sensory involvement; other times, it could be a completely immersive experience. Therefore, XR is like a spectrum that encompasses “the complete real” and “the complete virtual” concepts. It is an extension of human experiences relating to the perception of existence and possession of cognition.
What Is The History Of XR?
The inception of various ideological developments surrounding XR began in 1838 when Sir Charles Wheatstone, an English scientist of the Victorian Era, outlined “stereopsis” or “binocular vision” – where the brain combines two images, one from each eye, to make a single 3D image.
The stereoscopic display used in VR today to bring the feeling of depth to the digital images was an outcome of the concept of stereopsis.
Later in 1935, the idea of using goggles to traverse a fictional world was explored in the form of a novel by an American sci-fi writer named Stanley Weinbaum. This was the first prognosis of VR as we know it today.
Then between the 1950s and the 1970s, several other developments took place gradually in the various technologies that form XR together. Sensorama, the Headsight Headset, the first AR headset – The Sword of Damocles, and MIT’s Aspen Movie Map are trails to the Extended Reality technology.
Between the 1980s and 2000s, further developments in the field occurred. Several virtual and augmented reality companies came into existence. VPL Inc was the first company to sell VR goggles and gloves. VR arcade machines like the SEGA VR-1 motion simulator were another popular development in this era.
As for AR, in the 1990s, the introduction of an overlaying graphic over a real-world view gained popularity in sports broadcasting after the Sportsvision broadcast of a live NFL game in 1998.
And from the beginning of the 21st century, especially from 2010 to 2020, the momentum of advancements in the field rose. Products like Oculus Rift VR headset, Google Glass AR glasses, Microsoft’s HoloLens and many more widened the future scope of extended reality.
What Are The Components or Examples Of XR?
1. Virtual Reality or VR is one of the main pillars of extended reality. The virtual reality devices or media users experience a fully virtual environment, where their interactions and activities are all virtually based.
These fabricated graphical environments are mostly computer-generated, and real-life artificial objects are designed to add realism. Separate VR devices are needed to put users into this environment, providing them with a 360-degree view of the virtual world. These devices are designed to give a real illusion to users.
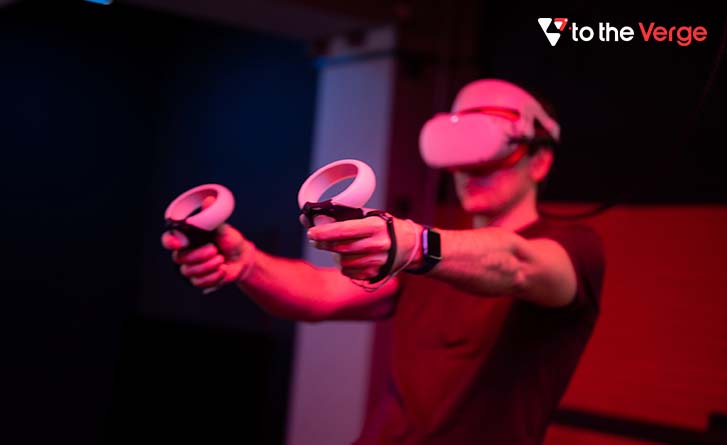

2. Augmented Reality or AR encapsulates virtual objects and imaginations put up in the real world to enhance real life. Augmented reality does not put the user into any virtual or computer-generated graphical environment; instead, it creates a perception of illusion in digital devices.
However, AR enables the users to interact in the real and virtual dimensions fully. One of the best examples to put this easily is Pokémon-GO which was a popular game that used augmented reality so that the players could interact with the real and graphical world through their smartphones and other mobile devices. Other examples of AR include the various filters on different social media and photo platforms that add some illusionary element to the content of the picture.
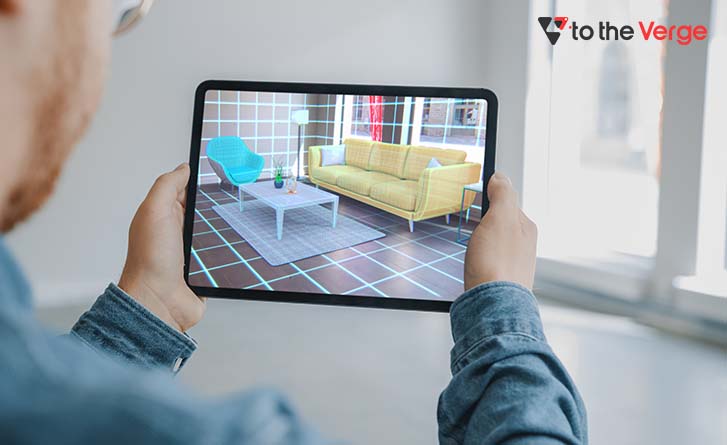

3. Mixed Reality or MR combines AR and VR, where one can interact with the digital and real world. Users can visualize their surroundings with the help of special Mixed Reality devices. These MR devices are more powerful and costlier than VR devices. They give users greater power to interact with their surroundings digitally.
For instance, putting on an MR device will provide the user with a view of their surrounding environment, wherein one may do general activities such as throwing a ball or closing the windows. These activities would be digitally executed in the MR headset, keeping the things undisturbed in actual reality.
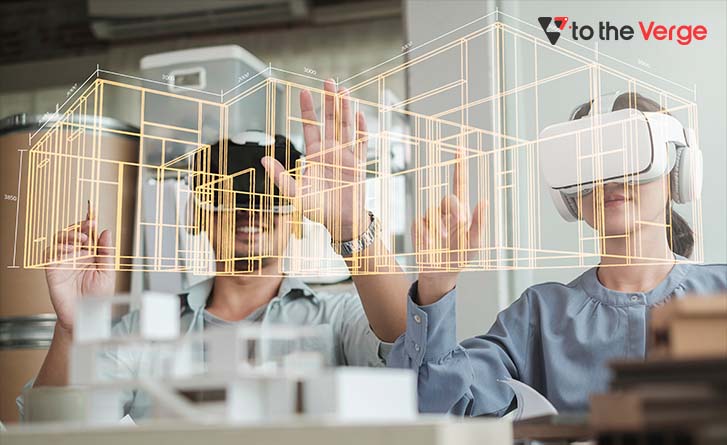

Applications Of Extended Reality
1. Extended Reality In Education
The use of extended reality in the education industry can prove to be extremely beneficial for students all across the globe. The technology could assist students in finding and choosing the right colleges. In addition, this technology could modernize and optimize distance education greatly by allowing students to enjoy global exposure.
AR and VR technology is being used to make the study material more interactive and interesting for the students, helping them understand and comprehend the subjects better.
2. Extended Reality In Health
Extended Reality in health provides medical education and surgical training to medical professionals. It allows medical students to practice techniques in life-like virtual environments repeatedly. Relative to traditional training models based on cadavers, virtual environments precisely simulate the living patients, mitigating error and promoting superior health outcomes.
VR in health offers experiential surgical education, helping surgeons increase their skill level. In addition, XR helps provide surgical support by letting surgeons visualize organs, tumors, X-rays, and ultrasounds in real-time and from multiple angles without diverting patient attention.
In addition, it also helps greatly in providing good patient care. Virtual reality systems have been designed to incorporate critical neuroscience and motor learning aspects to assist stroke survivors with motor recovery in stroke rehabilitation.
3. Extended Reality In Entertainment
XR in the entertainment can be utilized well, just like AR and VR. In addition, the entertainment industry can find new and amazing ways to use this technology and recreate classic cinema with greater immersion to woe the audience and old theatre fanatics.
4. Extended Reality In Marketing And Sales
Companies can utilize these technologies to advertise their product through extended reality technology, following virtual reality and augmented reality trends. In addition, they can give their users a hands-on experience of the products or services they might launch in the future to get constructive feedback.
5. Extended Reality In Real Estate And Housing
People can use extended reality in housing and real estate for house hunting. It will help people search for a house or an apartment suitable for them without traveling to different areas and spending a lot on brokerage. Similarly, owners can also find potential buyers from various locations, as there will be no need to go through physically. XR technology would limit or even eradicate the role of brokers in such a scenario.
6. Extended Reality For Work From Home Culture
The work-from-home culture can be significantly enhanced using extended reality technology. The employees and staff can visualize a live environment of their office or workplace and can attend meetings from their homes. It could be extremely beneficial in the case of remote working areas and remote training.
Future Of Extended Reality
The diverse and multiple applications enumerated above are considered only the tip of the iceberg of the future scope of extended reality. As extended reality companies continue to attract investments, expand and grow with time, the opportunities in XR will also increase in frequency and size.
However, the blurring of real and virtual boundaries puts issues of trust, privacy and sense of reality at the forefront. The technology’s mental, physical and social costs have been pondered upon to ensure extended reality is built and deployed responsibly and securely.
On the business side, tech companies are developing the foundational technologies required for XR; these include immersive 3D graphics, computer vision, machine learning, intuitive security, and 5G technologies. Different organizations contribute in their unique ways to promote a healthy ecosystem. In addition to the other lucrative opportunities, the most significant stance of XR’s future can be identified by its role in helping people access the metaverse. Jesse Alton, the founder of AngellXR, believes the XR will play a cross-functional role in the metaverse.
Challenges In Developing XR
- Cost: The XR devices are expensive. Many technologies work together, and a lot of hardware goes into making an entire kit to offer a realistic, immersive experience. If the price is higher, the common masses may not be able to use this product, and companies would not be able to increase their sales, consequently affecting further research and developments. Therefore, it becomes essential to cut the cost in any way possible to make the technology available and affordable for all. However, since the price depends on several other factors, this challenge becomes tricky.
- Hardware: Developing the hardware for XR devices is another challenge for companies because most of the technologies, software, & components used for making the hardware are expensive and difficult to procure. For XR to become popular and widely acceptable, the hardware should not just be robust and compact, efficiently processing a lot of information quickly and swiftly. XR also needs a disruptive revolution in display technology to show richer visual content and switch seamlessly between real and virtual worlds.
- Privacy: Privacy is a challenge that will be faced both by the users and the companies. Since XR devices must create an environment based on the user requirement, extended reality companies might need many private details to develop a user-rich climate. However, storage of such data can be costly on the company’s side, and the privacy and security of the information in XR will be a concern for the users.
FAQs – Extended Reality
Q.1 What Is The Purpose of Extended Reality?
The purpose of XR is to help modernize and optimize the technical and non-technical tasks in different sectors, increasing the overall productivity and efficiency of the industry.
Q.2 What Some Examples Of Extended Reality Companies?
Unity and Unreal are two gaming engine platforms that have extensively contributed to XR-friendly content creation. Apart from that, companies like Apple, Microsoft, SNAP, Nvidia, Google, and HTC Vive are a few among many other companies investing in the research and development of XR technologies like AR and VR.
Q.3 What Is The Difference Between Extended Reality and Mixed Reality?
XR combines three technologies, namely AR, VR, and MR. Its underlying principle is to make the digital world indistinguishable from the real world. It extends the sense of reality by blending the virtual and physical environments. On the other hand, MR is a hybrid reality. It goes beyond augmented reality, where the virtual world co-exists with the real world.
Key Takeaway On Extended Reality or XR
Extended Reality or XR is a combination of powerful technologies that would play a supportive role in developing extended reality metaverse. Trends in augmented and virtual reality are the building blocks that lead to the final picture of XR. As the world moves forward with these technologies, addressing the challenges of XR becomes a must to ensure that it will be accessible and affordable for the masses. If that is the case, the benefits of XR technology would be much more enjoyable.
- AR
- Augmented Reality
- Extended Reality
- Metaverse
- Mixed Reality
- MR
- MR devices
- Virtual reality
- VR
- XR
- XR Technology
Nitisha Lal is a writer enthusiastic and curious to learn new things. Currently, she writes about the latest developments in technology, particularly around Web3 and the Metaverse. She enjoys nature walks, capturing the world around her on the phone, or reading books when away from work.






![How to Update and Reinstall Keyboard Drivers on Windows 10/11 [A Guide]](https://wpcontent.totheverge.com/totheverge/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/05062841/How-to-Update-and-Re-install-Keyyboard-Drivers-on-Windows-10.jpg)
